Every day, search engines crawl billions of pages. However, they index fewer pages and display even fewer pages in their results. And if you can’t get your content in front of a search engine spider, the crawler will never find it.
In order to control how Google crawling and indexing your website, you must familiarize yourself with the specifics of Google Crawling and Indexing. Our blog post breaks down everything you need to know about this topic in order to fully optimize your website’s rank with this all-powerful search engine.
As Google sees it, the site is not just about what’s published on the site, but also about what is linked to from your site. If you want to control how Google crawls and indexes your web pages, you’ll need to start with a few basics.
- Add keyword-relevant meta titles and descriptions
- Add links in “alt” tags of images
- Generate sitemap and submit in search console
- Create robots.txt file to instruct search engine crawlers
- Crawl Management includes, crawl requesting, reducing Google bot crawl rate, and verifying Googlebot.
- Find canonical or duplicate pages and duplicate content
- Add Herflang tag for multilingual sites
When you turn on the Google crawling and indexing feature in Google Search Console, Google starts building an index of your site. The crawl rules are much more flexible than the default crawling rules, which are set for optimal performance.
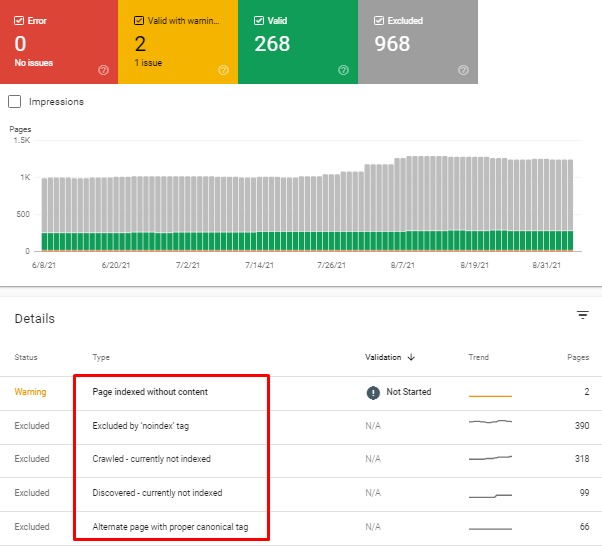
Effective Ways of Google Crawling And Indexing
The process of indexing and ranking begins the moment a website is crawled. By following SEO guidelines, you can directly influence how Google crawls and indexes your site. Improperly configured website crawling and indexing can cause all sorts of problems for your search engine ranking.
Here are some possible factors, which can control crawling and indexing
1. Page or Content Duplication
Make sure you know what canonical pages are and how they affect your site’s crawling and indexing. Content that is available on many URLs on the internet is referred to as duplicate content. As a result search engines are unable to determine which URL should appear higher in the search results and may rank both URLs lower and give other webpages precedence.
When it’s appropriate, you should also know how to remove or manage duplicate content on your site.
2. Resources
Make sure that any page, image, video, CSS files, etc., that Google is supposed to crawl in a site are accessible to Google. Also, ensure they are not blocked by robots.txt and that an anonymous user may access them.
Inaccessible pages will not display in the Index Coverage report, and they will be marked as not crawled in the URL Inspection tool too. You can only found blocked resources at the individual URL level, in the URL Inspection tool, blocked resources are only visible at the individual URL level. If important resources are blocked, Google may be unable to crawl the page.
To determine if Google sees the page as you expect, use the URL Inspection tool to render the live page. If found any blocked resources, be sure to fix them as soon as possible without disturbing the other factors.
3. Robots.txt
A robots.txt file can instruct search engine crawlers to which pages can or can’t request from your website. It helps to prevent selected pages from crawling such as duplicate pages, unnecessary resources like icons, logos, test pages, etc. You can use the “no index” tag to prevent indexing such resources which might overload your server with requests.
4. Sitemap
It is a file that allows search engines to crawl more effectively as it instructs which pages are more important in the website. Also, provides the complete information of update frequency textual and non-textual contents. Sitemap file amazingly coordinates with search engines in understanding your website structure and discover the pages to be crawled.
5. Site or Page Migration
Site migration is a process of implementing significant feature changes to a website, which usually results in a temporary loss of traffic. When transferring an entire site, do all of the necessary 301 redirections and sitemap adjustments, then notify Google, so that it can re-crawl the new site and passing your signals to it.
The same goes for the page migration! If you move a page to another temporarily, use 302 redirections instead of instructing Google to re-crawl the page. If permanent, implement 301 redirections and request for re-crawl in Google Search Console. If you remove any page temporarily or permanently, use the 404 status code, which indicates that the server can’t find the requested resource.
Best Practices Of Crawling & Indexing
- Make sure your links can be crawled. Only links with the proper tag and href attribute can be followed by Google. Google’s crawlers will not follow links that use other forms or tags without herf attribute due to scripted click events.
- Use rel=nofollow for paid or outbound links, to avoid sharing your quality signals with others.
- Manage your site crawling. If your site is likely a large website with hundreds of pages, use a strategic way to generatea sitemap with important pages, with help of robots.txt. Google may not crawl your hundreds of pages or took a long period to index, which may affect important page traffic as well.
- Using canonical tag help search engines to index the correct URL and avoid duplicate page/content.
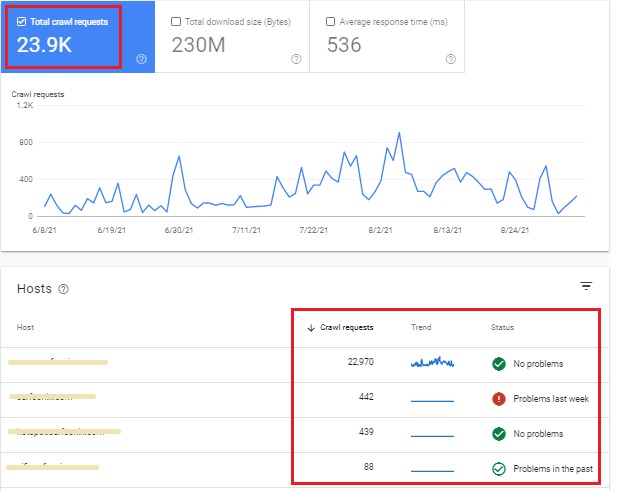
Follow the above guidelines when you want to control the Google crawling and indexing of your website, you will definitely get better results for all your important pages in organic results.
Whether you have any queries or need assistance, contact Devgraphix, the best digital marketing agency, offers custom solutions to enhance your website performance in search result pages.